?sort()
10^10
x <- c("hello", "hey", howdy)
x <- c("hello", "hey", "howdy")
str(x)
print(hello world)
y <- print("hello world")
data.frame(x, x)RStudio
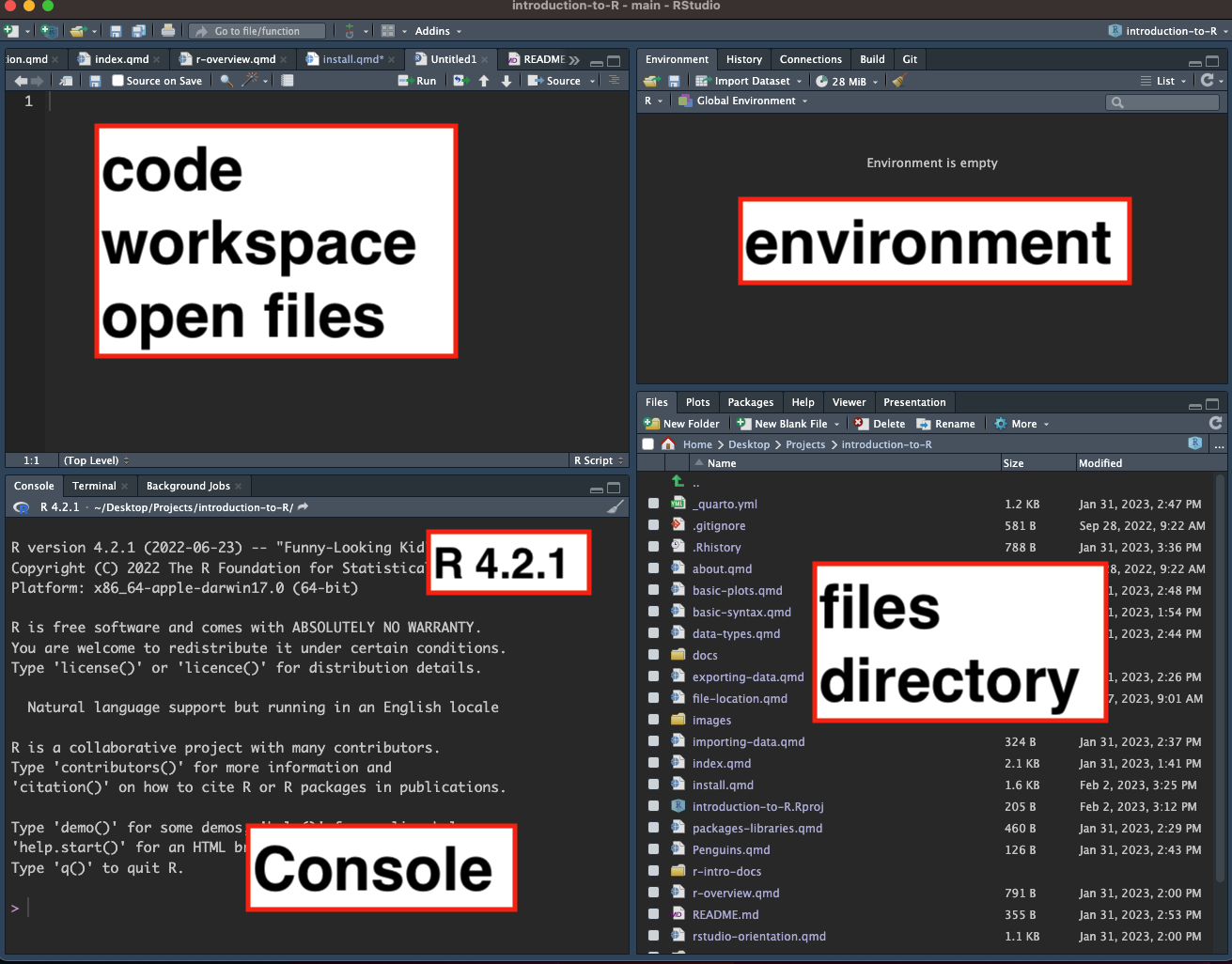
2 File structure & projects
Find where you have downloaded and sorted the
r-intro-docsdirectory. Navigate under Files in RStudio. See how the path is illustrated?Save a new R project as
introduction-to-Rin this directory.Close RStudio.
Navigate to where your R project is saved and open this file,
introduction-to-R.Rproj. This should automatically open RStudio and the files panel will open to this project directory.Open
r-intro-docs/intro.R. This is an R script. It looks like a text file. This is your primary workspace, where you can edit, document, and modify code. You execute each line by running the code.
3 Executing commands
The Rscript within Rstudio works like a raw text file, where most shortcut keys like copy/paste and home/end will work. As the course continues we will share what shortcut keys we often use - at any time you can also google “short cut keys RStudio for Mac” to find more.
In the script intro.R, place cursor next to one of the lines of code and run the command.
3.1 Mac
To run a command on a Mac, place cursor on the line you want to execute or highlight the code. Press COMMAND + ENTER.
3.2 PC
To run a command on a PC, place cursor on the line you want to execute or highlight the code. Press CONTROL + ENTER.
3.2.1 Activity
Practice executing the lines of code below. Document your code with information on what happens each time you execute a line.